Sphenoid Bone Called The Keystone Of The Cranial Floor

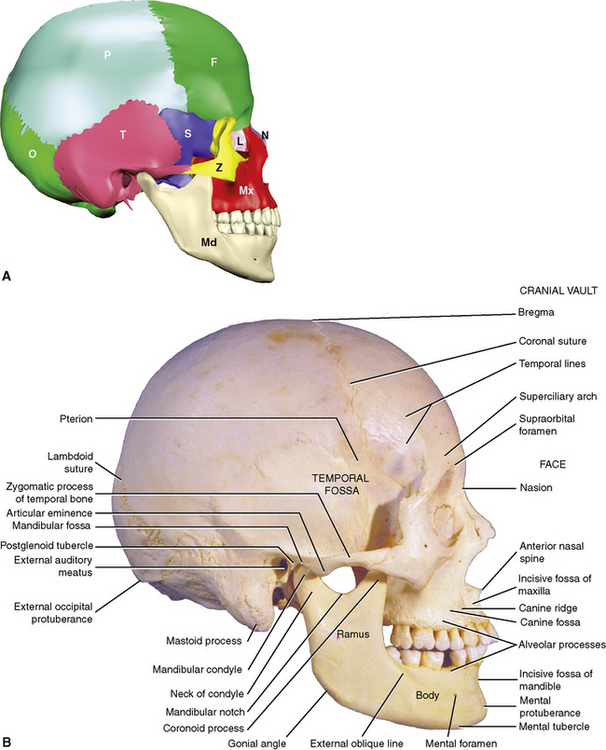
Frontal sphenoid zygomatic maxilla palatine lacrimal and ethmoid why can the sphenoid bone be called the keystone of the cranial floor forms a central wedge that articulates with all other cranial bones.
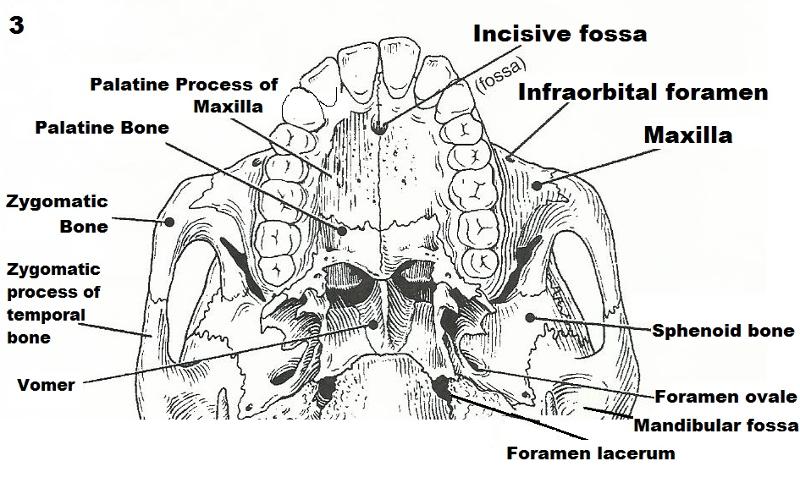
Sphenoid bone called the keystone of the cranial floor. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. One essential cranial bone is the sphenoid or the keystone of the. The sphenoid bone note 1 is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. Lies at the middle part of the base of the skull and is called the keystone of the cranial floor because it articulates with all the other cranial bones holding them all together.
Called the keystone of the cranial floor because it articulates with every other cranial bone ethmoid cranial bone anterior to sphenoid and posterior to nasal bones and contains foramina for olfactory cranial nerve coronal suture. The sphenoid bone has been called the keystone of the cranial floor since it is in contact with all of the. Sphenoid bone is called the keystone of the cranial floor because it articulates with all the other cranial bones holding them together. Contain a vertical groove that houses.
A prominent irregular wedge shaped bone at the base of the skull. Contains the sella turcica optic foramen and pterygoid processes sphenoid bone form the bridge of the nose nasal bones the smallest bones of the face. Posterior slightly. A prominent irregular wedge shaped bone at the base of the skull.
The sphenoid bone has been called the keystone of the cranial floor because it. Called the keystone of the cranial floor. Sphenoid bone is the large butterfly shaped compound bone at the base of the skull which containing a protective depression for the pituitary gland. There are 22 bones that can be found in the skull that can have different functions to protect the brain and other structures.
The sphenoid bone has been called the keystone of the cranial floor since it is in contact with all of the. The function of the skull is both structurally supportive and protective 2.